Geometry
Angles
A right angle is made up of 90 degreesA straight line is made up of 180 degrees.
If two lines intersect, the sum of the resulting four angles equals 360.
Polygons
A polygon is any figure with three or more sides (e.g., triangles, squares, octagons, etc.).Triangles
Area =
An isosceles right triangle (45-45-90) has sides in a ratio of x : x : x√2
A 30-60-90 triangle has sides in a ratio of x:x√3:2x, with the 1x side opposite the 30 degree angle.
An equilateral triangle has three equal sides. Each angle is equal to 60 degrees
Any given angle of a triangle corresponds to the length of the opposite side. The larger the degree measure of the angle, the larger the length of the opposite side.
A right triangle has a right angle (a 90 degree angle); the side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, and is always the longest side.
For a right triangle with legs A and B and hypotenuse C:
This is called the Pythagorean Theorem.
Each side of certain right triangles are integers. These sets of numbers are called Pythagorean triples, and you should memorize some of them: 3-4-5, 5-12-13, 8-15-17, 7-24-25. A multiple of a Pythagorean triple is a Pythagorean triple (e.g., 6-8-10).
The length of the longest side can never be greater than the sum of the two other sides.
The length of the shortest side can never be less than the positive difference of the other two sides.
Circles
A circle has 360 degrees. An arc is the portion of the circumference of a circle in x degrees of the circle.
A fraction of the circumference of a circle is called an arc. To find the degree measure of an arc, look at the central angle.
A chord is a line segment between two points on a circle. A chord that passes through the middle of the circle is a diameter.
If two inscribed angles hold the same chord, the two inscribed angles are equal.
An inscribed angle holding the diameter is a right angle (90 degrees).
Inscribed angles holding chords/arcs of equal length are equal:
Squares
Rectangles
Trapezoids
Quadrilaterals
The area of a square is s2 (s = side).
The diagonals of a square bisect one another, forming four 90 degree angles
The diagonals of a rhombus bisect one another, forming four 90 degree angles
The perimeter of a rectangle is twice its height plus twice its length (or, the sum of all its sides).
T
he area of a parallelogram can be found multiplying base x height (the base always forms a right angle with the height).
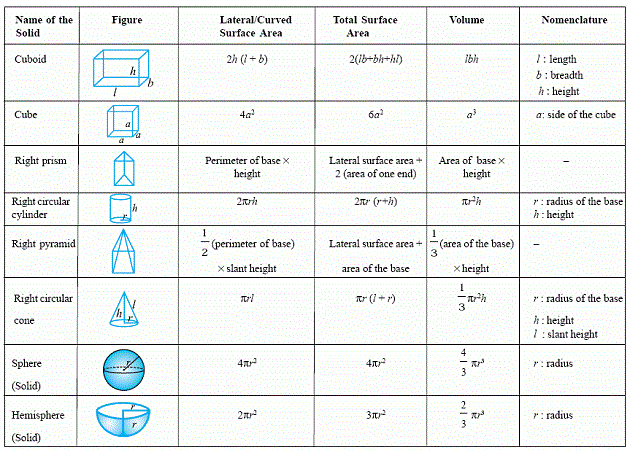
3-D Shapes
Cubes:
Rectangular Solids (including cubes):
Cylinders:
Coordinate Geometry
Lines
Any line can be represented by y=mx + c, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. This is called slope-intercept form.
The slope of a line can be found subtracting the y values of a pair of coordinates and dividing it by the difference in the x values:
To find the y-intercept plug in zero for x and solve for y
To find the x-intercept, plug in zero for y and solve for x
An equation like x = 3 is a vertical line at x = 3; an equation like y = 4 is a horizontal line at y = 4.
If given two points and asked to find the equation of a line that passes through them, first find the slope using the above formula, then plug one of the points into y = mx+b and solve for b.
The slopes of two lines which are perpendicular to each other are in the ratio of x : -1/x, where x is the slope of one of the lines (think: negative reciprocal).
The Distance Formula
For finding the distance between (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
Quadratics
The graph of a quadratic equation is a symmetrical shape called a parabola, which open upwards if a > 0 and down if a < 0.




















0 comments :
Post a Comment